Dr. Sagui Recent Publications
- Structural and Dynamical Properties of Nucleic Acid Hairpins Implicated in Trinucleotide Repeat Expansion Diseases. F Pan, P Xu, C Roland, C Sagui, K Weninger. Biomolecules, 14 (10), 1278, 2024.
Abstract: 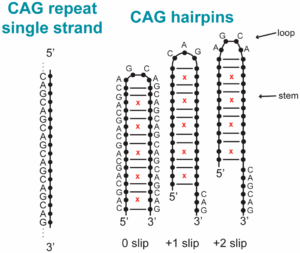 Dynamic mutations in some human genes containing trinucleotide repeats are associated with severe neurodegenerative and neuromuscular disorders—known as Trinucleotide (or Triplet) Repeat Expansion Diseases (TREDs)—which arise when the repeat number of triplets expands beyond a critical threshold. While the mechanisms causing the DNA triplet expansion are complex and remain largely unknown, it is now recognized that the expandable repeats lead to the formation of nucleotide configurations with atypical structural characteristics that play a crucial role in TREDs. These nonstandard nucleic acid forms include single-stranded hairpins, Z-DNA, triplex structures, G-quartets and slipped-stranded duplexes. Of these, hairpin structures are the most prolific and are associated with the largest number of TREDs and have therefore been the focus of recent single-molecule FRET experiments and molecular dynamics investigations. Here, we review the structural and dynamical properties of nucleic acid hairpins that have emerged from these studies and the implications for repeat expansion mechanisms. The focus will be on CAG, GAC, CTG and GTC hairpins and their stems, their atomistic structures, their stability, and the important role played by structural interrupts.
Dynamic mutations in some human genes containing trinucleotide repeats are associated with severe neurodegenerative and neuromuscular disorders—known as Trinucleotide (or Triplet) Repeat Expansion Diseases (TREDs)—which arise when the repeat number of triplets expands beyond a critical threshold. While the mechanisms causing the DNA triplet expansion are complex and remain largely unknown, it is now recognized that the expandable repeats lead to the formation of nucleotide configurations with atypical structural characteristics that play a crucial role in TREDs. These nonstandard nucleic acid forms include single-stranded hairpins, Z-DNA, triplex structures, G-quartets and slipped-stranded duplexes. Of these, hairpin structures are the most prolific and are associated with the largest number of TREDs and have therefore been the focus of recent single-molecule FRET experiments and molecular dynamics investigations. Here, we review the structural and dynamical properties of nucleic acid hairpins that have emerged from these studies and the implications for repeat expansion mechanisms. The focus will be on CAG, GAC, CTG and GTC hairpins and their stems, their atomistic structures, their stability, and the important role played by structural interrupts.
- Pathologic polyglutamine aggregation begins with a self-poisoning polymer crystal. Tej Kandola, Shriram Venkatesan, Jiahui Zhang, Brooklyn T Lerbakken, Alex Von Schulze, Jillian F Blanck, Jianzheng Wu, Jay R Unruh, Paula Berry, Jeffrey J Lange, Andrew C Box, Malcolm Cook, Celeste Sagui, Randal Halfmann. eLife, 12, RP86939, 2023.
Abstract: 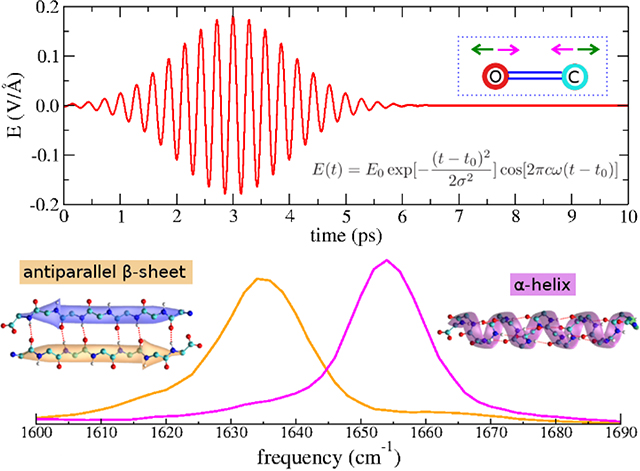 A long-standing goal of amyloid research has been to characterize the structural basis of the rate-determining nucleating event. However, the ephemeral nature of nucleation has made this goal unachievable with existing biochemistry, structural biology, and computational approaches. Here, we addressed that limitation for polyglutamine (polyQ), a polypeptide sequence that causes Huntington’s and other amyloid-associated neurodegenerative diseases when its length exceeds a characteristic threshold. To identify essential features of the polyQ amyloid nucleus, we used a direct intracellular reporter of self-association to quantify frequencies of amyloid appearance as a function of concentration, conformational templates, and rational polyQ sequence permutations. We found that nucleation of pathologically expanded polyQ involves segments of three glutamine (Q) residues at every other position. We demonstrate using molecular simulations that this pattern encodes a four-stranded steric zipper with interdigitated Q side chains. Once formed, the zipper poisoned its own growth by engaging naive polypeptides on orthogonal faces, in a fashion characteristic of polymer crystals with intramolecular nuclei. We further show that self-poisoning can be exploited to block amyloid formation, by genetically oligomerizing polyQ prior to nucleation. By uncovering the physical nature of the rate-limiting event for polyQ aggregation in cells, our findings elucidate the molecular etiology of polyQ diseases.
A long-standing goal of amyloid research has been to characterize the structural basis of the rate-determining nucleating event. However, the ephemeral nature of nucleation has made this goal unachievable with existing biochemistry, structural biology, and computational approaches. Here, we addressed that limitation for polyglutamine (polyQ), a polypeptide sequence that causes Huntington’s and other amyloid-associated neurodegenerative diseases when its length exceeds a characteristic threshold. To identify essential features of the polyQ amyloid nucleus, we used a direct intracellular reporter of self-association to quantify frequencies of amyloid appearance as a function of concentration, conformational templates, and rational polyQ sequence permutations. We found that nucleation of pathologically expanded polyQ involves segments of three glutamine (Q) residues at every other position. We demonstrate using molecular simulations that this pattern encodes a four-stranded steric zipper with interdigitated Q side chains. Once formed, the zipper poisoned its own growth by engaging naive polypeptides on orthogonal faces, in a fashion characteristic of polymer crystals with intramolecular nuclei. We further show that self-poisoning can be exploited to block amyloid formation, by genetically oligomerizing polyQ prior to nucleation. By uncovering the physical nature of the rate-limiting event for polyQ aggregation in cells, our findings elucidate the molecular etiology of polyQ diseases.
- Conformationally Restricted Glycopeptide Backbone Inhibits Gas-Phase H/D Scrambling between Glycan and Peptide Moieties. Christian Code, Danwen Qiu, Ilia A Solov’yov, Jung-Goo Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Shin, Christopher Roland, Celeste Sagui, Damian Houde, Kasper D Rand, Thomas JD Jørgensen. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 145 (44), 23925-23938, 2023.
Abstract: 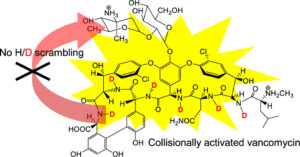 Protein glycosylation is a common post-translational modification on extracellular proteins. The conformational dynamics of several glycoproteins have been characterized by hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS). However, it is, in most cases, not possible to extract information about glycan conformation and dynamics due to the general difficulty of separating the deuterium content of the glycan from that of the peptide (in particular, for O-linked glycans). Here, we investigate whether the fragmentation of protonated glycopeptides by collision-induced dissociation (CID) can be used to determine the solution-specific deuterium content of the glycan. Central to this concept is that glycopeptides can undergo a facile loss of glycans upon CID, thereby allowing for the determination of their masses. However, an essential prerequisite is that hydrogen and deuterium (H/D) scrambling can be kept in check. Therefore, we have measured the degree of scrambling upon glycosidic bond cleavage in glycopeptides that differ in the conformational flexibility of their backbone and glycosylation pattern. Our results show that complete scrambling precedes the glycosidic bond cleavage in normal glycopeptides derived from a glycoprotein; i.e., all labile hydrogens have undergone positional randomization prior to loss of the glycan. In contrast, the glycosidic bond cleavage occurs without any scrambling in the glycopeptide antibiotic vancomycin, reflecting that the glycan cannot interact with the peptide moiety due to a conformationally restricted backbone as revealed by molecular dynamics simulations. Scrambling is also inhibited, albeit to a lesser degree, in the conformationally restricted glycopeptides ristocetin and its pseudoaglycone, demonstrating that scrambling depends on an intricate interplay between the flexibility and proximity of the glycan and the peptide backbone.
Protein glycosylation is a common post-translational modification on extracellular proteins. The conformational dynamics of several glycoproteins have been characterized by hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS). However, it is, in most cases, not possible to extract information about glycan conformation and dynamics due to the general difficulty of separating the deuterium content of the glycan from that of the peptide (in particular, for O-linked glycans). Here, we investigate whether the fragmentation of protonated glycopeptides by collision-induced dissociation (CID) can be used to determine the solution-specific deuterium content of the glycan. Central to this concept is that glycopeptides can undergo a facile loss of glycans upon CID, thereby allowing for the determination of their masses. However, an essential prerequisite is that hydrogen and deuterium (H/D) scrambling can be kept in check. Therefore, we have measured the degree of scrambling upon glycosidic bond cleavage in glycopeptides that differ in the conformational flexibility of their backbone and glycosylation pattern. Our results show that complete scrambling precedes the glycosidic bond cleavage in normal glycopeptides derived from a glycoprotein; i.e., all labile hydrogens have undergone positional randomization prior to loss of the glycan. In contrast, the glycosidic bond cleavage occurs without any scrambling in the glycopeptide antibiotic vancomycin, reflecting that the glycan cannot interact with the peptide moiety due to a conformationally restricted backbone as revealed by molecular dynamics simulations. Scrambling is also inhibited, albeit to a lesser degree, in the conformationally restricted glycopeptides ristocetin and its pseudoaglycone, demonstrating that scrambling depends on an intricate interplay between the flexibility and proximity of the glycan and the peptide backbone.
- Structure and Dynamics of DNA and RNA Double Helices Formed by d (CTG), d (GTC), r (CUG), and r (GUC) Trinucleotide Repeats and Associated DNA–RNA Hybrids. A Fakharzadeh, J Qu, F Pan, C Sagui, C Roland. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, B 127 (37), 7907-7924, 2023.
Abstract: Myotonic dystrophy type 1 is the most frequent form of muscular dystrophy in adults caused by an abnormal expansion of the CTG trinucleotide. Both the expanded DNA and the expanded CUG RNA transcript can fold into hairpins. Co-transcriptional formation of stable RNA·DNA hybrids can also enhance the instability of repeat tracts. We performed molecular dynamics simulations of homoduplexes associated with the disease, d(CTG)n and r(CUG)n, and their corresponding r(CAG)n:d(CTG)n and r(CUG)n:d(CAG)n hybrids that can form under bidirectional transcription and of non-pathological d(GTC)n and d(GUC)n homoduplexes. We characterized their conformations, stability, and dynamics and found that the U·U and T·T mismatches are dynamic, favoring anti–anti conformations inside the helical core, followed by anti–syn and syn–syn conformations. For DNA, the secondary minima in the non-expanding d(GTC)n helices are deeper, wider, and longer-lived than those in d(CTG)n, which constitutes another biophysical factor further differentiating the expanding and non-expanding sequences. The hybrid helices are closer to A-RNA, with the A-T and A-U pairs forming two stable Watson–Crick hydrogen bonds. The neutralizing ion distribution around the non-canonical pairs is also described.
- Unpolarized laser method for infrared spectrum calculation of amide I CO bonds in proteins using molecular dynamics simulation. VH Man, X He, PH Nguyen, C Sagui, C Roland, XQ Xie, J Wang. Computers in biology and medicine, 159, 106902, 2023.

Abstract: The investigation of the strong infrared (IR)-active amide I modes of peptides and proteins has received considerable attention because a wealth of detailed information on hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and the conformations of the peptide backbone can be derived from the amide I bands. The interpretation of experimental spectra typically requires substantial theoretical support, such as direct ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation or mixed quantum-classical description. However, considering the difficulties associated with these theoretical methods and their applications are limited in small peptides, it is highly desirable to develop a simple yet efficient approach for simulating the amide I modes of any large proteins in solution. In this work, we proposed a comprehensive computational method that extends the well-established molecular dynamics (MD) simulation method to include an unpolarized IR laser for exciting the CO bonds of proteins. We showed the amide I frequency corresponding to the frequency of the laser pulse which resonated with the CO bond vibration. At this frequency, the protein energy and the CO bond length fluctuation were maximized. Overall, the amide I bands of various single proteins and amyloids agreed well with experimental data. The method has been implemented into the AMBER simulation package, making it widely available to the scientific community. Additionally, the application of the method to simulate the transient amide I bands of amyloid fibrils during the IR laser-induced disassembly process was discussed in details.
- Frustration between preferred states of complementary trinucleotide repeat DNA hairpins anticorrelates with expansion disease propensity. P Xu, J Zhang, F Pan, C Mahn, C Roland, C Sagui, K Weninger. Journal of molecular biology, 435 (10), 168086, 2023.
Abstract: 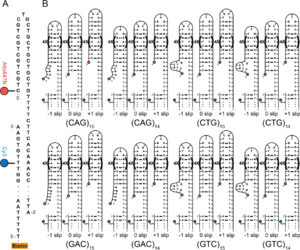 DNA trinucleotide repeat (TRs) expansion beyond a threshold often results in human neurodegenerative diseases. The mechanisms causing expansions remain unknown, although the tendency of TR ssDNA to self-associate into hairpins that slip along their length is widely presumed related. Here we apply single molecule FRET (smFRET) experiments and molecular dynamics simulations to determine conformational stabilities and slipping dynamics for CAG, CTG, GAC and GTC hairpins. Tetraloops are favored in CAG (89%), CTG (89%) and GTC (69%) while GAC favors triloops. We also determined that TTG interrupts near the loop in the CTG hairpin stabilize the hairpin against slipping. The different loop stabilities have implications for intermediate structures that may form when TR-containing duplex DNA opens. Opposing hairpins in the (CAG) ∙ (CTG) duplex would have matched stability whereas opposing hairpins in a (GAC) ∙ (GTC) duplex would have unmatched stability, introducing frustration in the (GAC) ∙ (GTC) opposing hairpins that could encourage their resolution to duplex DNA more rapidly than in (CAG) ∙ (CTG) structures. Given that the CAG and CTG TR can undergo large, disease-related expansion whereas the GAC and GTC sequences do not, these stability differences can inform and constrain models of expansion mechanisms of TR regions.
DNA trinucleotide repeat (TRs) expansion beyond a threshold often results in human neurodegenerative diseases. The mechanisms causing expansions remain unknown, although the tendency of TR ssDNA to self-associate into hairpins that slip along their length is widely presumed related. Here we apply single molecule FRET (smFRET) experiments and molecular dynamics simulations to determine conformational stabilities and slipping dynamics for CAG, CTG, GAC and GTC hairpins. Tetraloops are favored in CAG (89%), CTG (89%) and GTC (69%) while GAC favors triloops. We also determined that TTG interrupts near the loop in the CTG hairpin stabilize the hairpin against slipping. The different loop stabilities have implications for intermediate structures that may form when TR-containing duplex DNA opens. Opposing hairpins in the (CAG) ∙ (CTG) duplex would have matched stability whereas opposing hairpins in a (GAC) ∙ (GTC) duplex would have unmatched stability, introducing frustration in the (GAC) ∙ (GTC) opposing hairpins that could encourage their resolution to duplex DNA more rapidly than in (CAG) ∙ (CTG) structures. Given that the CAG and CTG TR can undergo large, disease-related expansion whereas the GAC and GTC sequences do not, these stability differences can inform and constrain models of expansion mechanisms of TR regions.
